Overview#
Whenever there is a patch submitted by a developer on Gerrithub, there might be a chance that a bug is introduced and the build might fail. These kind of logical/code quality errors might go unnoticed by the reviewer. These bugs can only be identified after it has been pushed to official repo and Travis CI catches the bugs.
This bot keeps monitoring for patches and tries to run a Travis CI test to identify these kind of bugs. The bot then updates the patch with Verified +1/-1 based on whether the patch is stable/unstable.
Architecture#
The overall architecture of the bot can be summarized as below:
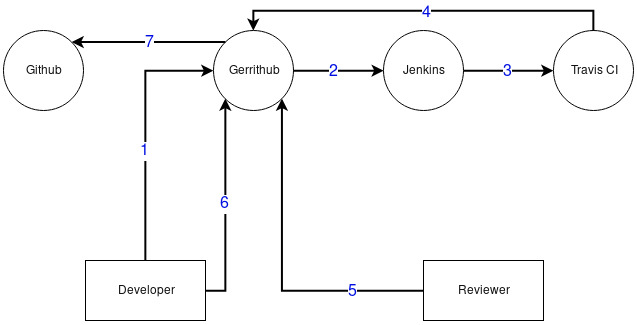
Pki-jenkins-bot-arch.jpg#
1 - Developer submits patch to GerritHub
2 - Jenkins listens for patches and triggers a job
3 - Jenkins job creates a throwaway branch and triggers Travis CI job
4 - Travis updates the label of the Gerrit patch. Adds comment with logs in case of Job failure
5 - Reviewer(s) review the code and mark success (Code-Review +1 or +2) or failure (return to step 1)
6 - Once patch receives Code-Review +2, the developer adds Workflow +1 and clicks on Submit
7 - Gerrithub pushes the patch to the official repo
Manual Steps to configure the bot#
Installing Jenkins and Required Plugins#
Install jenkins from official repo using the following command
\ ```http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins.repo <http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins.repo>`__\ ```https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key <https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key>`__Install java (open-jdk):
`` sudo dnf install -y java``
Make sure to start the jenkins server:
`` sudo systemctl start jenkins``
4. Setup jenkins admin user password by visiting http://localhost:8080/. The initial password is available at
/var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
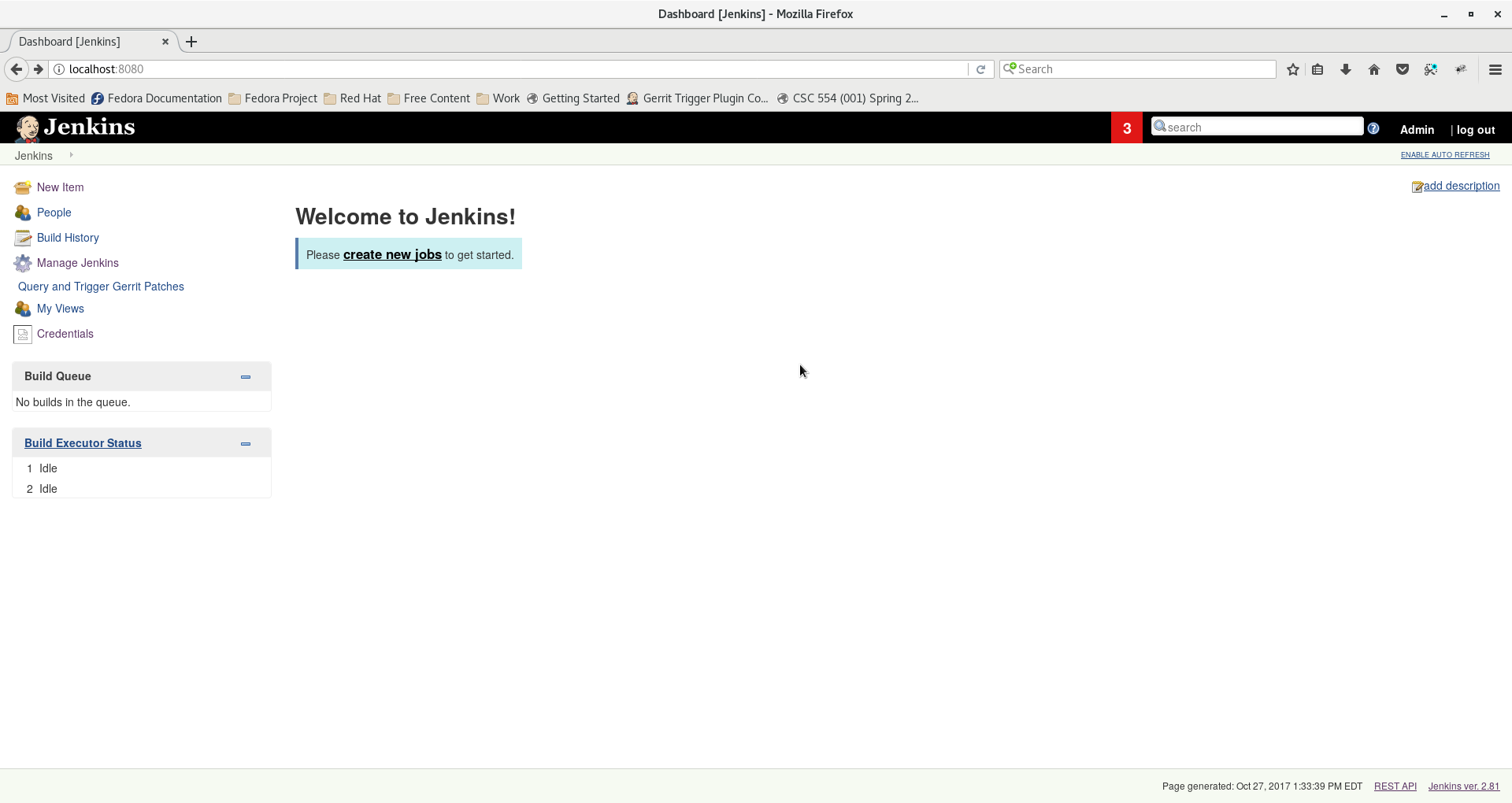
5. Click on Select plugins to install and select the following plugins and click Next:
github
ws-cleanup
credentials
gerrit-trigger
credentials-binding
plain-credentials
postbuild-task
envinject”
6. Provide the admin username and password and then click on Save and Finish
At this point you should have the following screen:
900px#
Creating SSH key for the bot#
Run ssh-keygen and generate a public-private key pair.
Have this handy as you’ll be using it in couple of next steps.
3. Add the public key to the pki-jenkins-bot user’s SSH keys in Github
Copy the generated keys to /var/lib/jenkins/.ssh
Configuring Gerrit server for PKI#
1. From Jenkins dashboard, click on Manage Jenkins from the left pane.
Select Gerrit Trigger.
Click on Add new server from the left pane.
4. Enter a name for the server and select Gerrit Server with Default Configurations
5. Enter the following configuration. Make sure to enter the password of the ssh key that you used in the previous step.
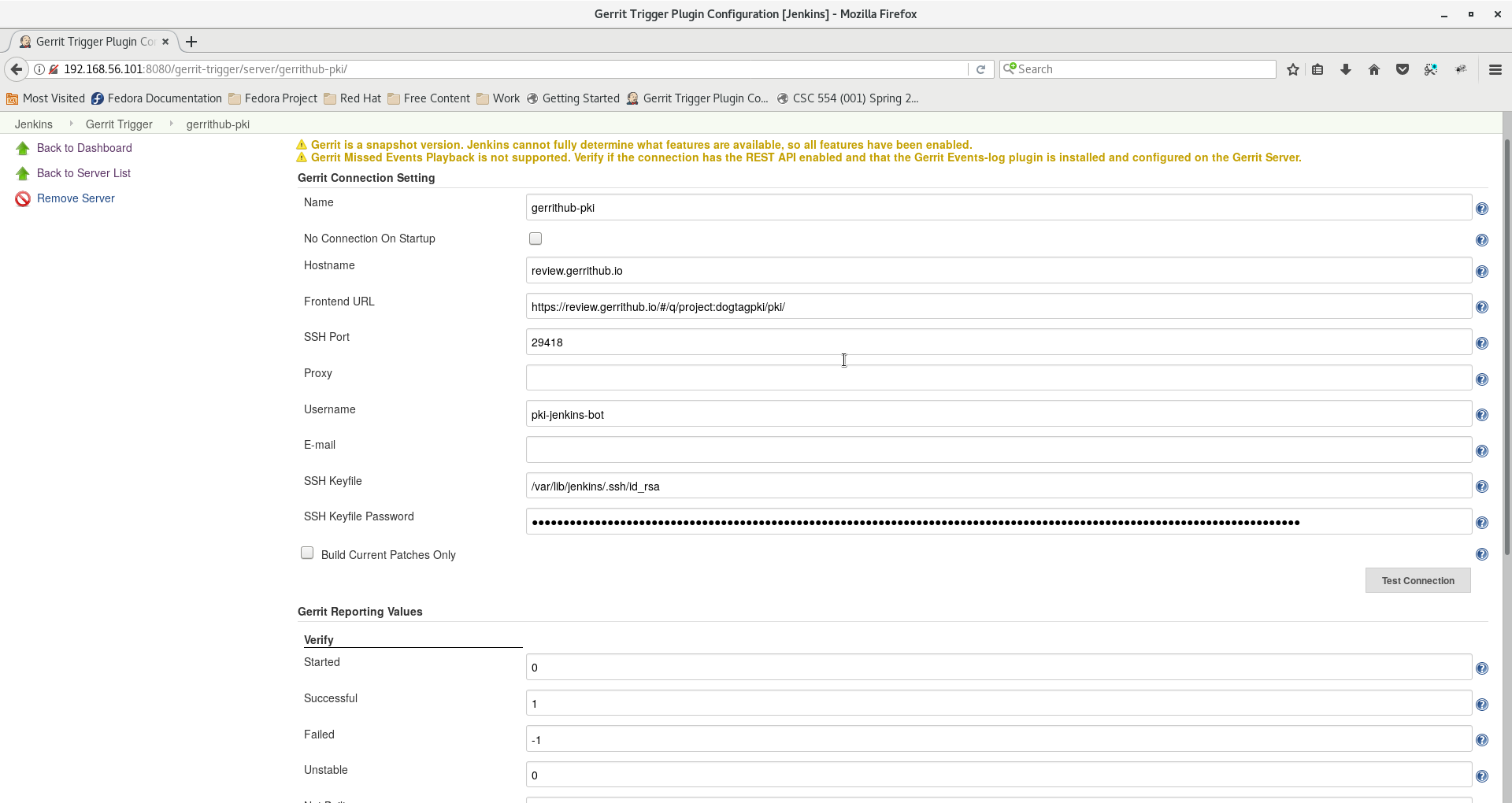
900px#
Click on Test connection to ensure the connection is successful.
Leave the default values
Click on Save.
9. Ensure that the small circle stays blue. If not, click on the small circle to bring it up.
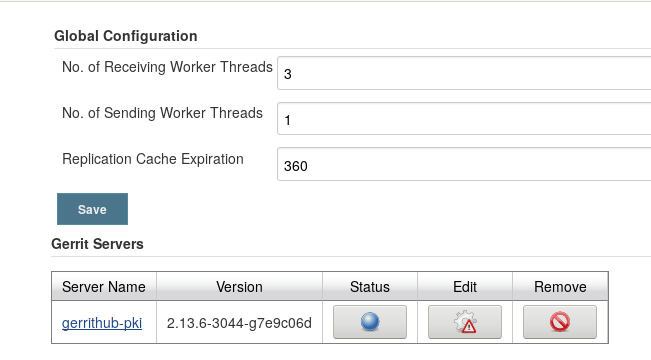
Gerrit-server-final.png#
Adding Github Token to the Jenkins#
Go to pki-jenkins-bot’s github profile.
Go to Settings > Developer Settings > Personal Access Tokens
3. Click on Generate new token and choose appropriate checkboxes and Click OK
4. Copy the generated token and keep it safe. This token once lost cannot be retrieved and has to be regenerated.
5. Go to Jenkins Dashboard. Click on Credentials > Jenkins > Global credentials (unrestricted) > Add Credentials (from left pane)
6. Select Secret Text from Kind and then enter the copied token in Secret. Enter github_token in the ID field.
Click OK.
Creating the pki-jenkins-bot job#
1. Create a new job by clicking on New Item on the left or Create new jobs link
2. Enter the name of the project and select Freestyle project. Click OK
Configure the project as the following:
Check Execute concurrent builds if necessary
Select Git under Source Code Management and enter the following URL. Here, pki-jenkins-bot is the username of the Github Account.
$GERRIT_SCHEME://pki-jenkins-bot@$GERRIT_HOST:$GERRIT_PORT/$GERRIT_PROJECT
Click on Add credentials -> Jenkins. In the window that pops up, choose SSH username with private key. Enter pki-jenkins-bot in the username and the private key that you generated in the previous instruction
Click on Advanced under the credentials and Enter $GERRIT_REFSPEC:$GERRIT_REFSPEC under Refspec
Enter $GERRIT_REFSPEC under Branch Specifier
Under Build Triggers check Gerrit Event and select the Gerrit server name you created in the previous step. Under Trigger on click Add and add Patchset created, Change Merged and Comment Added Contains Regular Expression and enter the value (?i)^(Patch Set [0-9]+:)?(nn)?s*brechecks*$ to trigger bot when comment “recheck” is added to the patch.
Under the Gerrit project, enter the project name as Type: Plain and Pattern: dogtagpki/pki and Branch Type: Path and Pattern: **
Under Build Environment, check Delete workspace before build, Inject environment variables to the build process - Under the groovy script, enter the following:
TimeZone.setDefault(TimeZone.getTimeZone('UTC'))def now = new Date()def map = [BRANCH_NAME: "bot_" + now.format("yyyyMMdd-HHmmss") + "_" + currentBuild['number']]return mapCheck “Use secret text(s) or file(s)” and add Secret Text. Enter the name as github_token and select the github_token created in the previous step.
Under Build, click on Add -> Execute Shell and enter the following script:
#create a temp branch and push it to official repossh-keyscan github.com >> $JENKINS_HOME/.ssh/known_hostsgit remote add bot git@github.com:pki-jenkins-bot/pki.gitgit checkout -b $BRANCH_NAMEgit push --set-upstream bot $BRANCH_NAMEpython $JENKINS_HOME/scripts/travisStatus.py -t $github_token -r pki-jenkins-bot/pki -b $BRANCH_NAMEUnder Post-build action, click on add and select Post build task. Enter the following script:
git push -d bot $BRANCH_NAME
Click on Save to save this job
Copy the Travis Py script#
In the Build step above, you would have added a line to execute Python script. You need to copy the file to the required location.
1. Obtain the copy of the Python script to monitor Travis from Github.
2.Copy to the Jenkins installations dir with the name travisStatus.py:
$JENKINS_HOME/scripts/travisStatus.py
Note: by default the $JENKINS_HOME points to /var/lib/jenkins
Retrigger build job for a patch#
To retrigger build on a patch that has already been build, add keyword recheck as a comment and publish it. The bot will be triggered automatically.
Patch build details and Build log analysis#
The jenkins build log can be accessed from the URL posted in the comments of the patch or directly from the Jenkins server link (You must be connected to the RedHat VPN)
The travis build can be accessed from bot’s Travis build https://travis-ci.org/pki-jenkins-bot/pki/builds
The temporary Github repo used to push patches for build is available at pki-jenkins-bot/pki
Note: This repo shouldn’t be cloned/used anywhere.
In case the build fails, the corresponding log will be uploaded to transfer.sh whose link can be obtained from the Travis log.
Ansible Playbook to automate#
Ansible playbook that automates all the above steps has been developed and is available in Github repo. Even though all these manual step are automated, certain steps that involve security have to be done manually. The repository includes README instructions on how to execute the Ansible Playbook.
Demonstration Video#
A general idea of how the bot works and a quick demo of the Bot setup using Ansible playbook is available on youtube.

Comments Added#
The following set of comments are added:
Build Status
Comment Added
Meaning
Started
Build started:
Jenkins has successfully picked up your patch and submitted a request for a Travis CI build
Build Started. Travis Build:
Travis has successfully started a build with the new patch
Successful
Verified+1 Travis Build Successful.
Travis Build was successful (ie) 2 jobs are successful
Failed
No Builds Executed
Something went wrong with Jenkins. Travis build won’t be exectuted. Try recheck option
Job # Failed Travis Job:
Logs:
The Job # has failed. The log URL is posted. The job URL is also included (2 jobs in total)
Jenkins is down. Restart the jenkins server